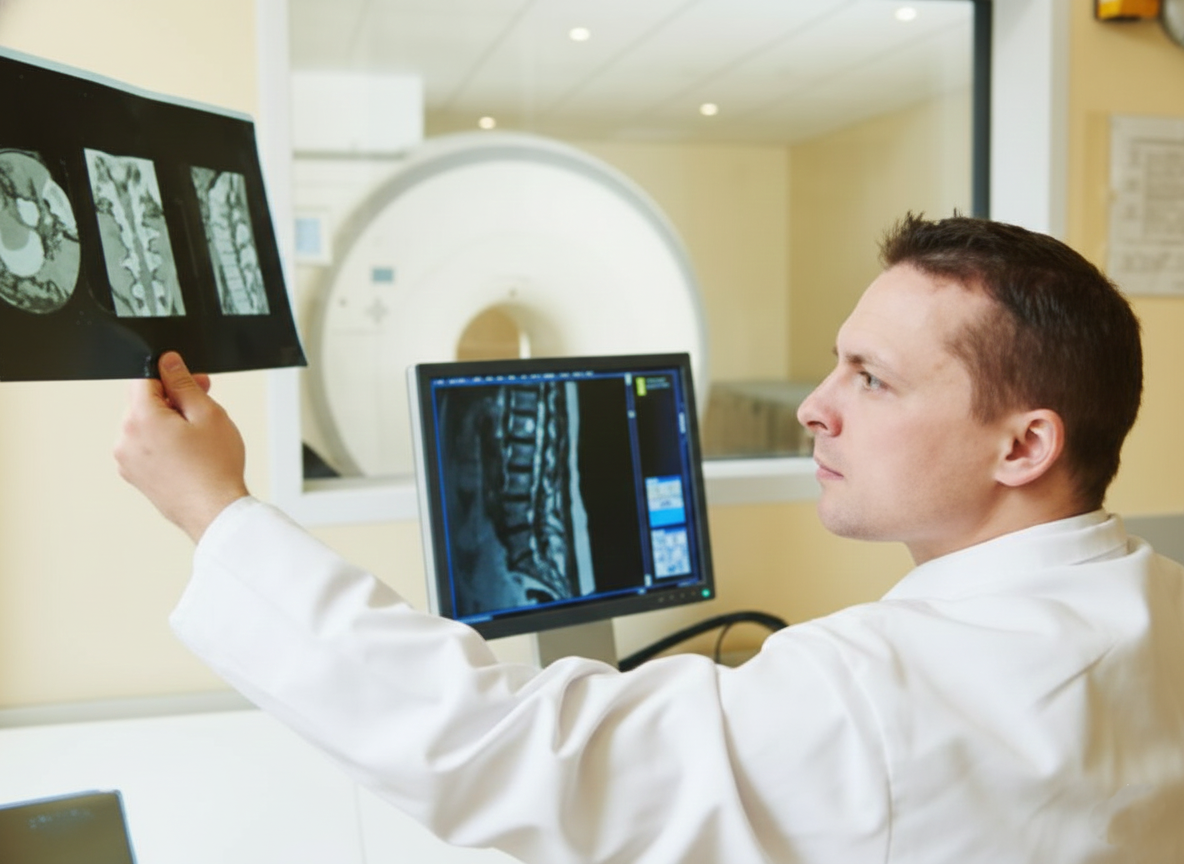
Orthopedic imaging tests play a crucial role in diagnosing and treating musculoskeletal conditions. Whether you’re dealing with a fracture, joint pain, or a degenerative disease like arthritis, accurate imaging is essential for pinpointing the problem and planning an effective treatment strategy. In this article, we’ll explore the most common types of orthopedic imaging tests used by healthcare professionals to assess bones, joints, and soft tissues.
Understanding Orthopedic Imaging Tests
Orthopedic imaging tests provide detailed visuals of bones, muscles, tendons, ligaments, and other structures within the musculoskeletal system. These tests are integral to orthopedic care, enabling doctors to diagnose issues accurately, monitor progress, and evaluate the effectiveness of treatments.
Why Orthopedic Imaging is Essential
- Accurate Diagnosis: Helps identify fractures, dislocations, and soft tissue injuries that may not be visible during a physical examination.
- Treatment Planning: Provides a clear view of the injury or condition, allowing doctors to devise an appropriate treatment plan.
- Monitoring: Tracks healing progress or the impact of treatments over time.
Types of orthopedic imaging tests and their applications
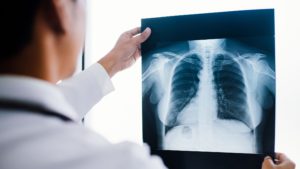
1. X-rays
X-rays are one of the most commonly used types of orthopedic tests due to their effectiveness in diagnosing bone injuries. They use electromagnetic radiation to capture images of bones and can reveal fractures, dislocations, and even some forms of arthritis.
When are X-rays Used?
- Fractures and Dislocations: X-rays are often the first imaging test ordered when a bone fracture or joint dislocation is suspected.
- Bone Tumors: These images can sometimes reveal abnormal growths or tumors in the bones.
- Arthritis: X-rays can show signs of joint degeneration and the presence of osteophytes (bone spurs) that are common in osteoarthritis.
Pros:
- Quick and painless.
- Widely available and cost-effective.
- Provides immediate results for bone injuries.
Cons:
- Limited to hard tissues like bones and can’t effectively visualize soft tissues.
- Exposure to a small amount of radiation, which can be a concern for repeated use over time.

2. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MRI uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to create highly detailed images of soft tissues, making it one of the best types of orthopedic tests for evaluating muscles, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage.
When are MRIs Used?
- Soft Tissue Injuries: MRIs are excellent for diagnosing ligament tears (such as ACL injuries), muscle strains, and tendon injuries.
- Spinal Conditions: This imaging test is often used for assessing conditions like herniated discs and spinal stenosis.
- Joint Disorders: MRIs can reveal joint damage caused by conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
Pros:
- No exposure to radiation.
- Provides high-resolution images of soft tissues.
- Can capture detailed images from multiple angles.
Cons:
- More expensive and time-consuming than X-rays.
- Not suitable for patients with metal implants or pacemakers due to the strong magnetic field.
- Some patients may experience discomfort or claustrophobia during the test.
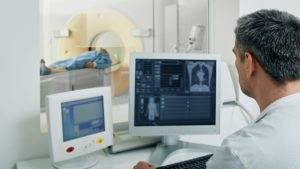
3. Computed Tomography (CT) Scans
CT scans combine X-ray images taken from different angles to create cross-sectional views of the body. This test provides a more detailed look at bones and soft tissues compared to traditional X-rays and is particularly useful in complex cases where a higher level of detail is required.
When are CT Scans Used?
- Complex Fractures: CT scans offer detailed images of fractures, particularly those in complex areas like the spine or pelvis.
- Bone and Joint Disorders: They can be used to assess bone tumors, infections, and degenerative joint diseases.
- Surgical Planning: CT scans provide a 3D view that helps surgeons plan for orthopedic procedures.
Pros:
- Produces detailed images of both bones and soft tissues.
- Provides cross-sectional views for a more comprehensive assessment.
- Faster than MRI, making it suitable for emergency situations.
Cons:
- Higher radiation exposure compared to standard X-rays.
- May require the use of contrast dye, which can cause allergic reactions in some patients.
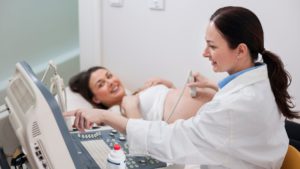
4. Ultrasound
Ultrasound imaging, also known as sonography, uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of soft tissues in real time. This test is particularly useful for evaluating soft tissue injuries and guiding certain procedures, like injections.
When is Ultrasound Used?
- Tendon and Ligament Injuries: Ultrasounds can assess injuries in tendons and ligaments, such as rotator cuff tears and Achilles tendon ruptures.
- Joint Inflammation: It can detect inflammation in joints, often used in cases of arthritis and bursitis.
- Fluid Accumulation: Useful for identifying fluid buildup in joints or tissues, which may indicate injury or infection.
Pros:
- No radiation exposure, making it safe for all patients, including pregnant women.
- Real-time imaging allows for dynamic assessment, especially in sports injuries.
- Non-invasive and generally cost-effective.
Cons:
- Limited to soft tissue visualization and cannot penetrate bones.
- Operator-dependent, meaning image quality can vary based on the technician’s skill.

5. Bone Scans
Bone scans involve injecting a small amount of radioactive material into the bloodstream, which then accumulates in areas of high bone activity. This imaging test is sensitive to bone metabolism and can detect issues that may not appear on other types of orthopedic tests.
When are Bone Scans Used?
- Detecting Bone Infections: Effective for diagnosing osteomyelitis, a bone infection that can be challenging to detect with other imaging methods.
- Identifying Fractures Not Visible on X-rays: Useful for stress fractures and small fractures that may be missed on traditional X-rays.
- Cancer Diagnosis and Monitoring: Bone scans can detect the spread of cancer to bones and monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
Pros:
- Highly sensitive for detecting bone abnormalities.
- Useful for diagnosing conditions that other tests may miss.
- Provides insights into bone metabolism and activity.
Cons:
- Involves exposure to a small amount of radioactive material.
- Time-consuming, as the radioactive substance needs time to circulate before imaging.
- Can produce false positives, necessitating additional tests for confirmation.
Conclusion
Orthopedic imaging tests are essential for accurately diagnosing and managing musculoskeletal conditions. Whether it’s a basic X-ray or a more advanced MRI or CT scan, each type of test offers unique benefits suited to specific conditions. If you’re experiencing symptoms or have suffered an injury, consult with an orthopedic specialist to determine the most appropriate imaging test for your situation. By choosing the right type of orthopedic test, you and your healthcare provider can better understand your condition and create an effective treatment plan to support your recovery.